React + WebSockets to Create Real-Time Dashboards
Real-time dashboards are everywhere today:
- Stock traders rely on millisecond updates.
- IoT companies monitor sensor data streams.
- DevOps teams watch live server logs.
Polling APIs every few seconds isn’t enough, it wastes resources and still feels sluggish.
Instead, we use websockets in React: a protocol that keeps a persistent two-way connection between client and server. This means data flows instantly as soon as it’s available.
But when you build React Dashboards, raw speed isn’t enough. If you don’t focus on React Performance Optimization properly, your app will:
- Lag as datasets grow.
- Crash browsers if you render thousands of points.
- Waste CPU with unnecessary re-renders.
In this article, we’ll learn how to:
- Set up a React WebSocket hook
- Stream and render live data in charts.
- Apply performance optimization so the UI stays smooth.
Step 1: Establishing a WebSocket Connection
We use a custom hook to encapsulate the logic rather than spreading it. Libraries like react-use-websocket are preferred by many developers because they make it easier to use websocket in React without the need for boilerplate code.
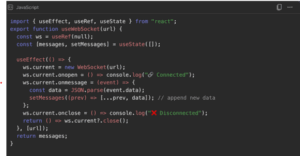
Why this design?
- UseRef for WebSocket instance → prevents reconnection on re-renders.
- useEffect dependency on url → reconnects only when URL changes.
- setMessages with spread → keeps history of incoming data.
- Cleanup on unmount → avoids zombie WebSocket connections.
Many developers quickly discover that handling connections and reconnection logic can become complicated when experimenting with WebSockets in React. Clean abstractions are extremely useful because of this.
Step 2: Rendering Data in Real-Time
Now, let’s visualize WebSocket data. Assume the backend sends JSON like:
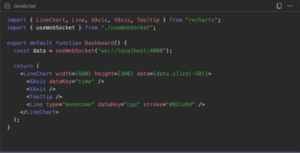
We can plot it in our React dashboards using Recharts. One of the most frequent use cases for developers investigating react websocket integration is the production of real-time charts.
IoT device monitoring is another effective use case for websocket in React, when dependable and immediate updates are required.
Why slice(-50)?
Without limiting, data would grow infinitely → memory bloat & rendering lag. By keeping only the
last 50 points, we ensure:
- Charts stay lightweight.
- User still sees the latest trends.
If your use case requires history, store older data separately (e.g., in Indexed DB or server logs).
Step 3: Performance Optimization
A naive implementation works for a few dozen messages, but will break when updates come
hundreds per second. Let’s optimize.
1. Batch Updates with a Buffer
Every set State triggers a render. If you call it on every WebSocket message, React will choke. Instead, buffer messages in a ref, then flush them at intervals:
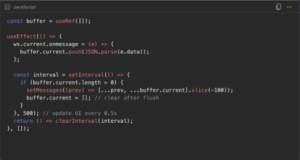
Benefits:
- Browser handles thousands of messages/sec without choking.
- UI updates feel smooth (humans can’t perceive sub-100ms updates anyway).
Batching updates is essential when creating WebSockets in React dashboards that contain server logs or high-frequency trading data.
2. Avoid Unnecessary Re-Renders
Charts can be expensive to redraw. Use memorization:
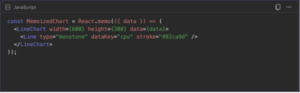
Now, the chart re-renders only when data actually changes, not when parent state
updates.
3. Virtualize Large Tables / Logs
If your React Dashboards shows logs or transactions, rendering thousands of <div>s kills
performance.
Solution: virtualization — render only visible rows.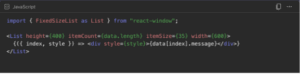
A list with 10,000 rows feels as fast as 100 rows.
4. Offload Heavy Computations
If incoming data needs aggregation (e.g., rolling averages, anomaly detection), don’t block
React Options:
- Use Web Workers for heavy calculations.
- Or pre-compute stats on the server before streaming.
React Performance Optimization focuses strongly on this strategy. When using React Websocket, this method is particularly crucial because poorly optimized calculations have the potential to cause the interface to freeze.
5. Connection Management
- Reconnect on failures:
Implement exponential backoff retries when WebSocket closes unexpectedly.
- Heartbeat messages:
Send pings every 30s to detect dead connections.
- Authentication:
Pass JWT tokens during connection upgrade if dashboard is user-specific.
Stability when scaling websocket across numerous dashboard WebSocket in React is ensured by robust connection handling.
Wrapping Up
By combining React + WebSockets, you can build dashboards that update instantly and scale gracefully.
Key takeaways:
- Encapsulate React WebSocket hook or Use react-use-websocket for cleaner code
- Limit how much data you keep in memory.
- Batch updates instead of updating on every message.
- Use memoization & virtualization to keep React lean.
- Offload heavy processing to Web Workers or backend.
All of these strategies will ensure that your dashboards are not only real-time but also seamless. If you’re still learning how to use WebSocket in React, keep in mind that your project will be future-proof with clear abstractions and astute optimizations.
 End to End Technology Solutions
End to End Technology Solutions
